Invoking a Lambda Function
What are we going to do?
This tutorial will walk you through how to use the “Invoking a Lambda Function” feature.
We will assume you have:
- installed Service Catalog Puppet correctly
- bootstrapped a spoke
- created a manifest file
- added an account to the manifest file
We are going to perform the following steps to “Invoking a Lambda Function”:
- set up an AWS IAM role in the spoke account
- create a sample lambda function
- add a lambda invoke to the manifest file
During this process you will check your progress by verifying what the framework is doing at each step.
Step by step guide
Here are the steps you need to follow to “Invoking a Lambda Function”
Set Up an AWS IAM Role in the Spoke Account
This guide assumes that a role exists within the spoke account that can be assumed by the Service Catalog Tools account. The name of this role would need to be the same across all spoke accounts, and the role would need permissions appropriate for your lambda function(s) to be able to complete its tasks. For the purpose of this example, a CloudFormation template has been provided that you can use to create the role in the spoke account that will allow our sample lambda function to run successfully.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Description: "IAM Role in spoke accounts that will have trust relationship with Service Catalog Tools account."
Parameters:
ToolsAccountId:
Description: "The Service Catalog Tools AWS Account ID"
Type: String
ToolsAccountAccessRole:
Description: "Name of the IAM role that the management account will be allowed to assume"
Default: ToolsAccountAccessRole
Type: String
Resources:
AssumedRole:
Type: AWS::IAM::Role
Description: |
IAM Role needed by the Service Catalog Tools Account
Properties:
RoleName: !Ref ToolsAccountAccessRole
Policies:
- PolicyName: ToolsAccountTrustPolicy
PolicyDocument:
Version: 2012-10-17
Statement:
- Effect: Allow
Action: 'iam:*'
Resource: '*'
AssumeRolePolicyDocument:
Version: "2012-10-17"
Statement:
- Effect: "Allow"
Principal:
AWS: !Sub "arn:aws:iam::${ToolsAccountId}:root"
Action:
- "sts:AssumeRole"
Creating the sample lambda function
We will need to create the AWS Lambda function that will be executed by the framework. This function will exist in the account where you have installed the Service Catalog Tools. When you want to perform an action in a spoke account you should read the account_id and region properties from the event object. If you want to use parameters they are available using the parameters attribute in the event object.
-
You should save the following into a file named create-iam-group-lambda.yaml
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09' Description: Creates a Lambda function that assumes a role into spoke accounts and creates an IAM group Resources: rLambdaCustomRole: Type: AWS::IAM::Role Properties: AssumeRolePolicyDocument: Version: 2012-10-17 Statement: - Effect: Allow Principal: Service: [lambda.amazonaws.com] Action: - sts:AssumeRole ManagedPolicyArns: - !Ref rLambdaCustomPolicy rLambdaCustomPolicy: Type: AWS::IAM::ManagedPolicy Properties: PolicyDocument: Version: 2012-10-17 Statement: - Effect: Allow Action: ['logs:CreateLogGroup', 'logs:CreateLogStream', 'logs:PutLogEvents'] Resource: !Sub arn:${AWS::Partition}:logs:${AWS::Region}:${AWS::AccountId}:log-group:* - Effect: Allow Action: - sts:AssumeRole Resource: "*" rLambda: Type: AWS::Lambda::Function Properties: FunctionName: create-iam-group Description: Creates an IAM Group Handler: index.lambda_handler Code: ZipFile: | import json import boto3 # Set up clients sts = boto3.client('sts') def get_session_info(event): acct_id = event['account_id'] role_name = event['parameters']['RoleName'] role_arn = 'arn:aws:iam::' + acct_id + ':role/' + role_name sts_response = sts.assume_role( RoleArn=role_arn, RoleSessionName='LambdaInvokeSession' ) return sts_response def lambda_handler(event, context): print(event) sts_response = get_session_info(event) access_key = sts_response["Credentials"]["AccessKeyId"] secret_key = sts_response["Credentials"]["SecretAccessKey"] session_token = sts_response["Credentials"]["SessionToken"] iam = boto3.client( 'iam', aws_access_key_id=access_key, aws_secret_access_key=secret_key, aws_session_token=session_token ) group_name = 'sc-tools-invoke-lambda-test-group' response = iam.create_group( GroupName=group_name ) MemorySize: 128 Role: !GetAtt rLambdaCustomRole.Arn Runtime: python3.7 Timeout: 300 Outputs: LambdaName: Value: !Ref rLambda -
You should then use AWS CloudFormation to create a stack named create-iam-group-lambda using the template you just created
What did we just do?
- You created an AWS CloudFormation template
- You used the template to create a stack in CloudFormation
- The stack created a sample lambda function
Adding a lambda-invocation to the manifest
Now we are ready to add a lambda invocation to the manifest file.
-
Navigate to the ServiceCatalogPuppet CodeCommit repository
-
Click the ServiceCatalogPuppet repository
-
Click the link to the manifest.yaml file, and then click the Edit button
-
Add the following snippet to the end of the main input field:
lambda-invocations:
create-iam-group:
function_name: create-iam-group
qualifier: $LATEST
invocation_type: Event
parameters:
RoleName:
default: "ToolsAccountAccessRole"
invoke_for:
tags:
- regions: "default_region"
tag: "type:prod"
- The main input field should look like this:
accounts:
- account_id: "<YOUR_SPOKE_ACCOUNT_ID_WITHOUT_HYPHENS>"
name: "puppet-account"
default_region: "eu-west-1"
regions_enabled:
- "eu-west-1"
- "eu-west-2"
tags:
- "type:prod"
- "partition:eu"
lambda-invocations:
create-iam-group:
function_name: create-iam-group
qualifier: $LATEST
invocation_type: Event
parameters:
RoleName:
default: "ToolsAccountAccessRole"
invoke_for:
tags:
- regions: "default_region"
tag: "type:prod"
Committing the manifest file
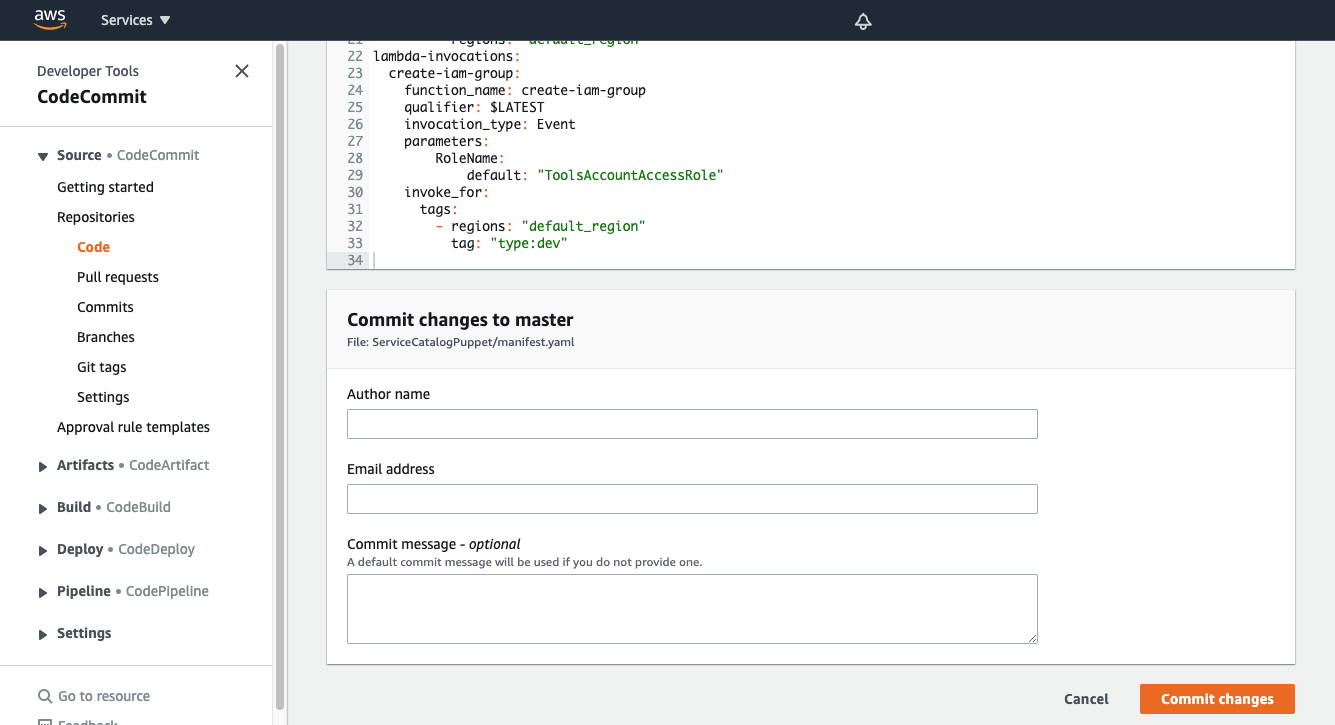
Now that we have updated the manifest file we are ready to commit our changes.
- Set your Author name
- Set your Email address
- Set your Commit message
Using a good / unique commit message will help you understand what is going on later.
- Click the Commit changes button:
Verifying the lambda invocation
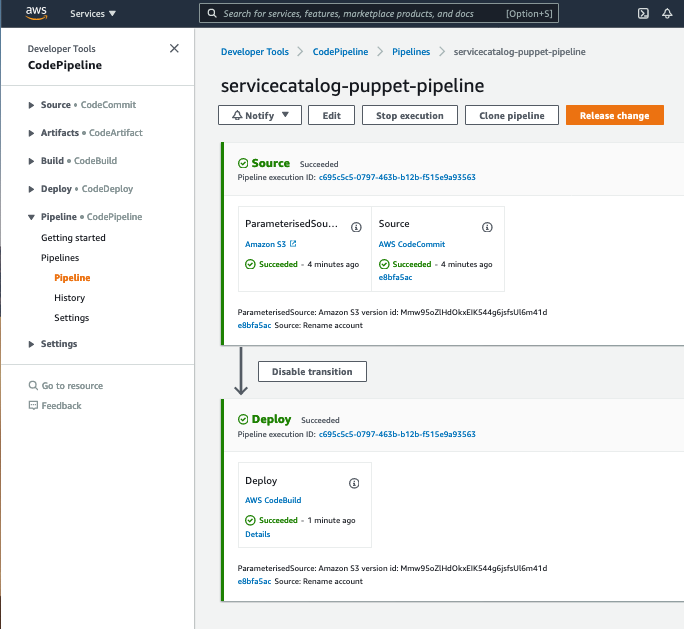
Once you have made your changes the ServiceCatalogPuppet Pipeline should have run or if you were quick may still be running. If it has not yet started feel free to the hit the Release change button.
Once it has completed it should show the Source and Deploy stages in green to indicate they have completed successfully:
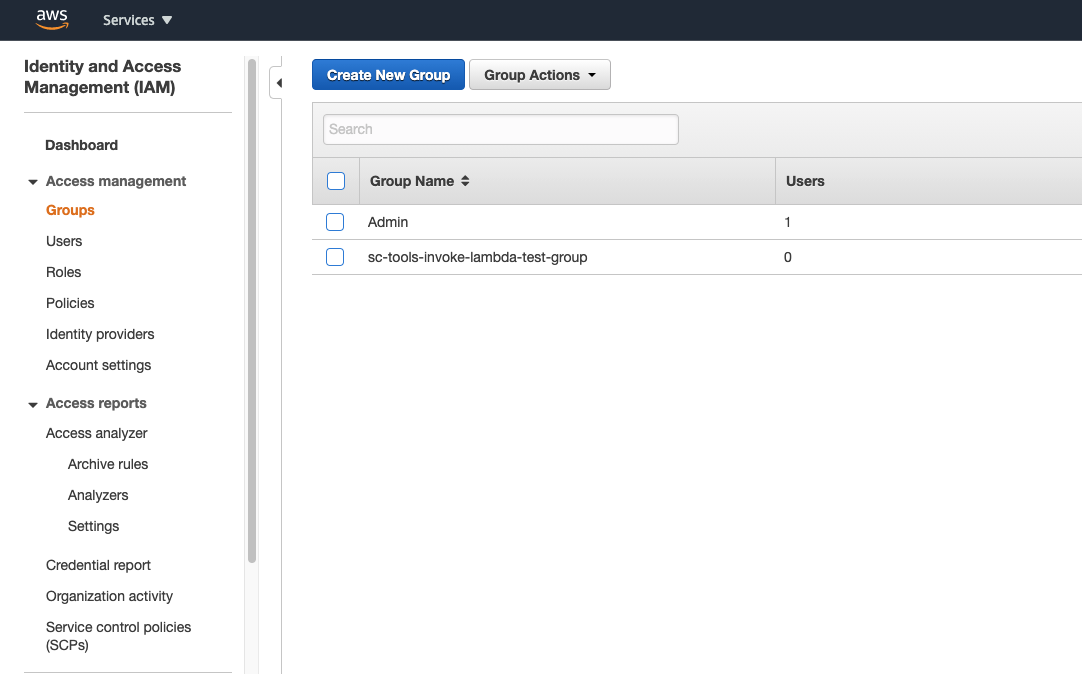
Once you have verified the pipeline has run you can go to IAM Groups Console in the spoke account to view the IAM Group created by the lambda invoke labeled sc-tools-invoke-lambda-test-group.
You have now successfully invoked a lambda function!